VR APPS ONLINE!

Virtual reality and augmented reality did take longer than expected to become popular in the realm of gaming and entertainment. While that is largely changing now with better headsets from tech giants Google, Facebook, and even Apple, VR and AR are thriving in another industry altogether – manufacturing.
A report from the industry think tank Research and Markets predicts that the revenue of the AR and VR market is expected to reach $55 billion by 2021 A huge portion of this stems from the wide adoption in the manufacturing industry The same report estimates that VR applications in manufacturing alone will increase by a staggering 98.9% between 2017 and 2021. That’s why companies like Facebook, owner of Oculus, have launched their line of products specifically for business and industrial use cases.
The rapidly evolving use-cases of both AR and VR are enabling the industry to reach growth in an unprecedented manner. Here’s how:
Manufacturers are increasingly investing in VR and AR tools and applications to train their employees. VR and AR let you digitally enhance your environment either through overlaying items on what you see or, in the case of VR, immersing you in a computer generated environment.
This enables companies to give more immersive and sensory training – especially in critical areas that require higher quality and more stringent safety standards. And it’s backed by science. A recent study from the University of Maryland notes that people training through VR environments retain much more information than those who train with traditional methods.
People learn better in virtual environments because of the high level of immersion that comes with the medium. In this kind of trainings, workers only focus on the content that is shown to them. This can prevent any form of distraction while the training appeals to more senses than conventional methods. That’s why companies like Chevron and Walmart are investing in VR training facilities to catalyze the training, upskilling, and reskilling of their employees.
One huge advantage that AR gives manufacturers, however, is the increased precision and accuracy that these technologies afford their factory floors. Remote assistance, laying out complex resources, and guiding workers through vital processes are the most sought after industrial use cases of AR and VR today. Industries like PCB making and chip manufacturing need highly skilled employees, as even minor mistakes can incur huge costs to organizations.
Chip manufacturer giant GlobalFoundries has recently partnered with AR startup PTC to help workers skilfully navigate their extremely costly machinery through superimposed animations. This is expected to improve performance on the factory floors and expand business outcomes.
PCB manufacturers are also following suit. A finished circuit board includes many different components that must be arranged correctly in a very limited space. If you look at the number of PCB parts and the challenge of arranging the parts on the small circuit board, you can see that AR has great potential to compensate for human error.
Paired with custom PCB design tools, manufacturing in this space is quickly improving to keep up with demand for new and innovative products.
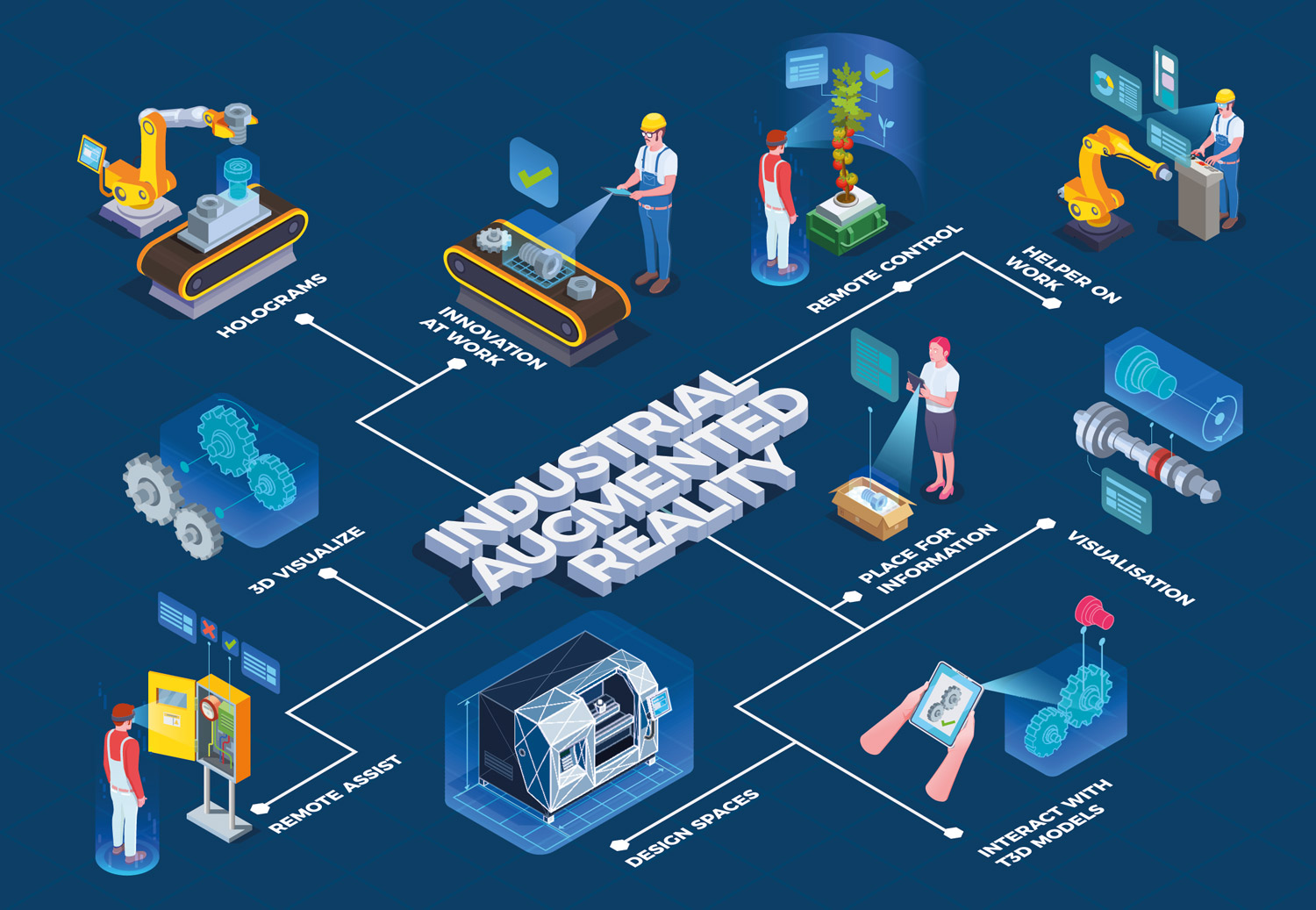
VR and AR also give manufacturers the opportunity to train people in environments that are otherwise impossible, because these are either far too risky or far too expensive.
Workplace accidents cost manufacturers billions of dollars each year. These emerging technologies, however, have the potential to prevent or help deal with accidents and therefore reduce the human and monetary costs of these incidents.
High-risk manufacturing sectors have begun using VR to train their employees not only to minimize accidents, but also to learn emergency procedures. Chevron and Japan Airways use VR environments and AR glasses to train technicians in standardized protocols for emergency repairs and aftercare. Pacific Gas and Electric technicians use VR glasses for valve assembly training.
While there’s definitely an upfront cost in investing in these technologies, it has the potential to save organizations money in the long run. Large enterprises are beginning to see the huge value proposition of adopting these technologies to drive innovation and increase efficiency.
About the author:
Bryan Matthews is a freelance tech writer. His primary focus is on how modern technology is shaping the workforce, supply chain, and the global economy. Traveling around the world he hopes to bring to his readers informed articles on the latest global tech trends. In his free time, he is an avid reader.
Contributed post
Register for free and start editing!